The Metric System - Compiled and edited by Shankar Dhungel
What is Metric System?
The metric system is a system of measurement that uses the meter, liter, and gram as base units of length (distance), capacity (volume), and weight (mass) respectively.
To measure smaller or larger quantities, we use units derived from the metric units
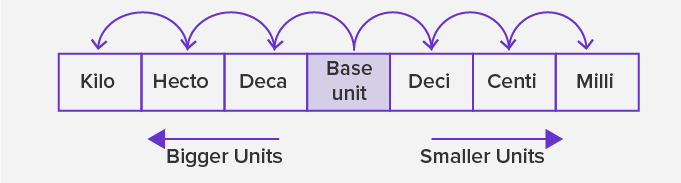
- The given figure shows the arrangement of the metric units, which are smaller or bigger than the base unit.
- The units to the right of the base unit are smaller than the base unit. As we move to the right, each unit is 10 times smaller or one-tenth of the unit to its left. So, a ‘deci’ means one-tenth of the base unit, ‘centi’ is one-tenth of ‘deci’ or one-hundredth of the base unit and ‘milli’ is one-tenth of ‘centi’ or one-thousandth of the base unit.
- The units to the left of the base unit are bigger than the base unit. As we move to the left, each unit is 10 times greater than the unit to its right. So, a ‘deca’ means ten times of the base unit, ‘hecto’ is ten times of ‘deca’ or hundred times of the base unit and ‘killo’ is ten times of ‘hecto’ or thousand times of the base unit.
Kilo
|
Hecto
|
Deca
|
Base Unit
|
Deci
|
Centi
|
Milli
|
1000
|
100
|
10
|
1
|
1/10
|
1/100
|
1/1000
|
So, the units for length, weight (mass) and capacity(volume) in the metric system are:
Length: Millimeter (mm), Decimeter (dm), Centimeter (cm), Meter (m), and Kilometer (km) are used to measure how long or wide or tall an object is.
Examples include measuring the thickness or length of debit card, length of cloth, or distance between two cities.
Kilometer
(km)
|
Hectometer
(hm)
|
Decameter
(dam)
|
Meter
(m)
|
Decimeter
(dm)
|
Centimeter
(cm)
|
Millimeter
(mm)
|
1000
|
100
|
10
|
1
|
1/10
|
1/100
|
1/1000
|
Weight: Gram (g) and Kilogram(kg) are used to measure how heavy an object, using instruments.
Examples include measuring weight of fruits or, our own body weight.
Kilogram
(kg)
|
Hectogram
(hg)
|
Decagram
(dag)
|
Gram
(g)
|
Decigram
(dg)
|
Centigram
(cg)
|
Milligram
(mg)
|
1000
|
100
|
10
|
1
|
1/10
|
1/100
|
1/1000
|
Capacity: Milliliter (ml) and Liter (l) are used to measure how much quantity of liquid an object can hold.
Examples include measuring the amount of juice in a juice can, or amount of water of in a water tank.
Kiloliter
(kl)
|
Hectoliter
(hl)
|
Decaliter
(dal)
|
Liter
(l)
|
Deciliter
(dl)
|
Centiliter
(cl)
|
Milliliter
(ml)
|
1000
|
100
|
10
|
1
|
1/10
|
1/100
|
1/1000
|
Metric Conversions: Meters, grams and liters are considered the base units of length, weight and volume, respectively.

Here’s how we can multiply or divide for making metric conversions. To convert a bigger unit to the smaller unit, we move left to write, we multiple by 10. Moving right to left, from smaller unit to bigger, we divide by 10.
Now, let's have an understanding about the following tables:
Let us look at some examples of converting from one unit to another.
Example 1: Convert 5 km to m.
As 1 km = 1000 m
Therefore, 5 km = 5 × 1000 = 5000 m
Example 2: Convert 250 kg to milligrams.
We know, 1 g = 1000 mg and 1 kg = 1000 g
So, we first convert the kg to g as:
1 kg = 1000 g
Therefore, 250 kg = 250 × 1000 g = 250,000 g
Now, converting g to mg:
1 g = 1000 mg, therefore: 250,000 g = 250,000 × 1000 mg = 250,000,000 mg
Example 3: Convert 250 ml to liters.
1 liter = 1000 ml
Therefore, 450 ml = 450 ÷ 1000 = 0.45 liter
The US Standard Units or the Customary System uses customary units.
This system measures:
Length or distance in inches, feet, yards, and miles.
Capacity or volume in fluid ounces, cups, pints, quarts or gallons.
Weight or mass in ounces, pounds and tons.
What is Length?
Length is the term used for identifying the size of an object or distance from one point to Length is a measure of how long an object is or the distance between two points. It is used for identifying the size of an object or distance from one point to another. The length of an object is its extended dimension, that is, its longest side. For example, the length of the ruler in the picture is 15 cm.

Here, the arrow above the ruler
denotes the length of the ruler as it is the longest side of the ruler.
Different units of length
The standard unit of length based on the metric system is a meter (m). According to the length that needs to be measured, we can convert a meter into various units like millimeters (mm), centimeter (cm), and kilometer (km).
Centimeters and millimeters help measure smaller lengths and meters and kilometers help measure larger lengths like distance. For example, the length of the pencils can be calculated in centimeters (cm), while kilometers can measure the distance between two buildings or places.
One hundred equal divisions of a meter give a centimeter. It is written as ‘cm’. That is,
1 m = 100 cm
One thousand equal divisions of kilometer give a meter. That is,
1 km = 1,000 m
According to the length conversion charts, the different units of lengths and their equivalents are given below:
A kilometer (km), meter (m), and centimeter (cm) are the commonly used units of length.
Conversion of these units is done using the given formula.

Additionally, in the customary system (followed in the United States) inches, feet, yards, and miles are used as the unit for length.
The relation between the customary units is given below:

Metric system and customary system
With the assortment of various units, the metric system seems quite a logical system as compared to the customary system and converting units in the metric system is much simpler than converting them in the customary system.




0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home